Angular Nested and Wildcard Validation
In this section we will go through a in-depth example on how to validate complex forms that contain nested objects and array of objects.
The form that we aim to validate looks like the following.
Components Structure
To be able to proceed with the implementation, the form needs to be divided into components. The image below shows the different components used for the example.
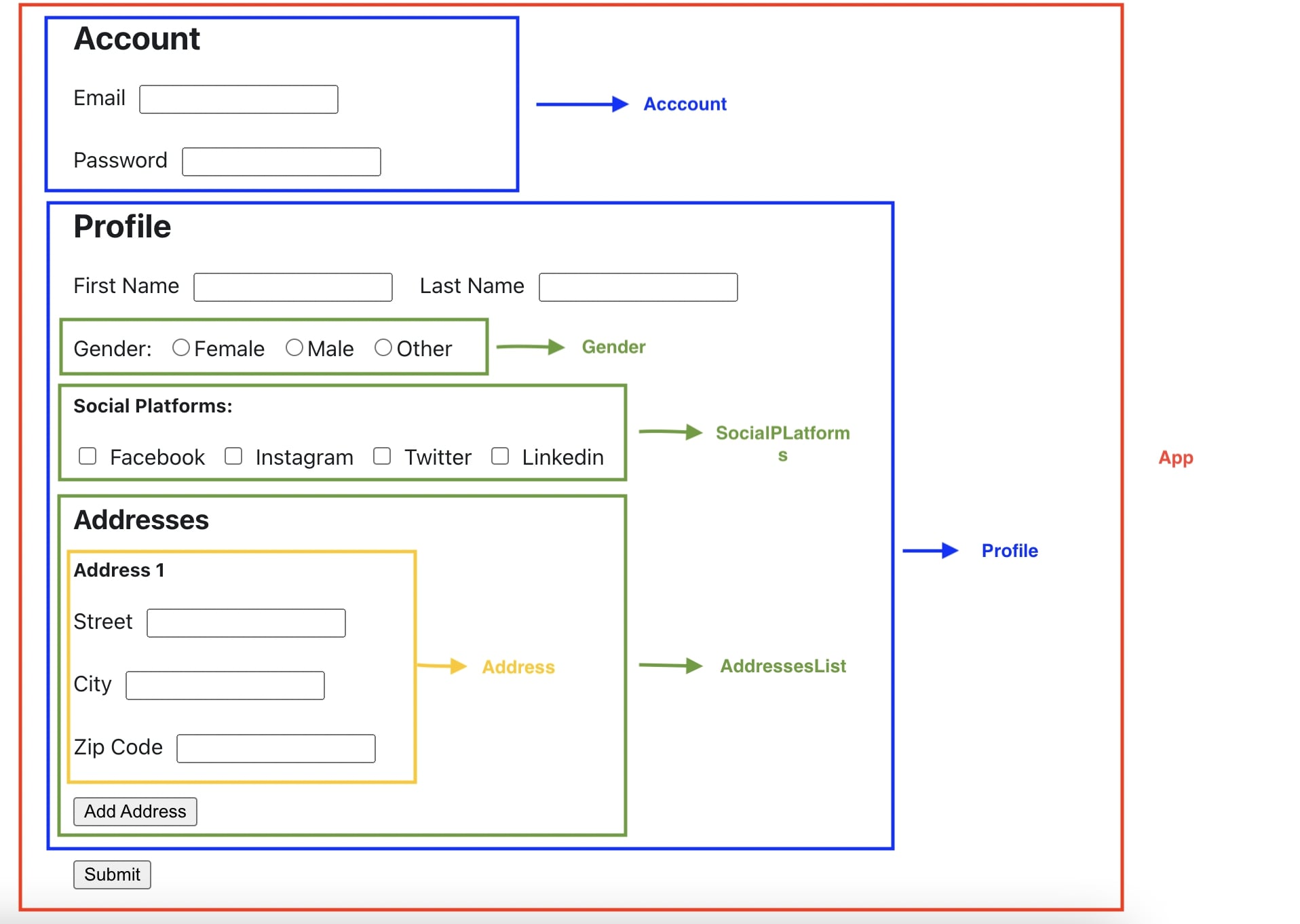
validationError.service.ts
The first step to be done before creating any component, is to create a service that will hold the ErrorBag
instance to be used in all the components. That way the errors can be imported directly in the component instead of being passed from parent to child components.
Go ahead and create a validationError.service.ts file in the services directory.
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { ErrorBag } from 'simple-body-validator';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class ValidationErrorService {
errors: ErrorBag = new ErrorBag();
setErrors(errors: ErrorBag){
this.errors = errors;
}
getErrors(): ErrorBag {
return this.errors;
}
}
styles.css
Let's define some basic css entries to be used in the form templates.
.mr-10 {
margin-right: 10px;
}
.mr-20 {
margin-right: 20px;
}
.mb-20 {
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.cl-red {
color: red;
}
.inline {
display: inline-block;
}
App Component
The app.component.ts will be used to set the inital data, rules, and to pass them to the validator instance.
Let's start with the imports
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { FormGroup, FormControl, FormArray } from '@angular/forms';
import {
make,
ruleIn,
Password,
Validator,
InitialRules,
} from 'simple-body-validator';
import { ValidationErrorService } from './services/validationError.service';
Next, we will specify the inital data attributes, along with their respective rules. You can find all the available rules here.
export class AppComponent implements OnInit {
constructor(private validationErrorService: ValidationErrorService) {}
// Create a new validator instance
validator: Validator = make();
// Specify the needed rules
rules: InitialRules = {
email: 'required|email',
password: ['required', Password.default()],
profile: {
firstName: 'required|string|min:3|max:30',
lastName: 'required|string|min:3|max:30',
// Gender must match one of the predefined values
gender: ['required', ruleIn(['Female', 'Male', 'Other'])],
// The social platform must an array of min 2 items, max 3 items,
// and each item must match one of the predefined values
socialPlatforms: 'bail|array|min:2|max:4',
'socialPlatforms.*': ruleIn([
'Facebook',
'Instagram',
'Linkedin',
'Twitter',
]),
// The address must be an array with at least one item
addresses: 'required|array|min:1',
// Each item in the addresses array must be an object,
'addresses.*': 'object',
// validate the attributes for each address object
'addresses.*.street': 'required|string|min:5|max:255',
// The city is required when zip code doesn't exist
'addresses.*.city': [
'required_without:profile.addresses.*.zipCode',
'string',
'min:5',
'max:255',
],
// The zip Code is required when city doesn't exist
'addresses.*.zipCode': [
'required_without:profile.addresses.*.city',
'digits:5',
],
},
};
// Set the initial form data
form = new FormGroup({
email: new FormControl(''),
password: new FormControl(''),
profile: new FormGroup({
firstName: new FormControl(''),
lastName: new FormControl(''),
gender: new FormControl(''),
socialPlatforms: new FormControl([]),
addresses: new FormArray([
new FormGroup({
street: new FormControl(''),
city: new FormControl(''),
zipCode: new FormControl(''),
}),
]),
}),
});
}
If you take a look at the rules object you will notice that it matches exactly the structure of the data
object. Additionally, to validate the array attributes we used the * notation, and in the city validation you might have
noticed the following.
'required_without:profile.addresses.*.zipCode',
In the required_without rule we specified the full path of the attribute, otherwise the library will not be able to
map the rule to the correct attribute value. You can find an introduction on Nested and Wildcard rules here.
Now we will use the ngOnInit lifecycle method to pass the initial data and rules to the validator instance,
and to set the error instance on the validationError service.
ngOnInit() {
// Set initial data and rules
this.validator.setData(this.form.value)
.setRules(this.rules)
.setCustomMessages({
socialPlatforms: {
min: 'You must at least select :min platforms',
},
});
// Set the ErrorBag insance in the validationErrorService
this.validationErrorService.setErrors(this.validator.errors());
}
Set Custom Messages
The setCustomMessages method can be used to override the message generated by the library. To find out more on
Customizing Error Messages click here.
- TS
- HTML
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { FormGroup, FormControl, FormArray } from '@angular/forms';
import {
make,
ruleIn,
Password,
Validator,
InitialRules,
} from 'simple-body-validator';
import { ValidationErrorService } from './services/validationError.service';
@Component({
selector: 'my-app',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css'],
})
export class AppComponent implements OnInit {
constructor(private validationErrorService: ValidationErrorService) {}
// Create a new validator instance
validator: Validator = make();
// Specify the needed rules
rules: InitialRules = {
email: 'required|email',
password: ['required', Password.default()],
profile: {
firstName: 'required|string|min:3|max:30',
lastName: 'required|string|min:3|max:30',
gender: ['required', ruleIn(['Female', 'Male', 'Other'])],
socialPlatforms: 'bail|array|min:2|max:4',
'socialPlatforms.*': ruleIn([
'Facebook',
'Instagram',
'Linkedin',
'Twitter',
]),
addresses: 'required|array|min:1',
'addresses.*': 'object',
'addresses.*.street': 'required|string|min:5|max:255',
'addresses.*.city': [
'required_without:profile.addresses.*.zipCode',
'string',
'min:5',
'max:255',
],
'addresses.*.zipCode': [
'required_without:profile.addresses.*.city',
'digits:5',
],
},
};
// Set the initial form data
form = new FormGroup({
email: new FormControl(''),
password: new FormControl(''),
profile: new FormGroup({
firstName: new FormControl(''),
lastName: new FormControl(''),
gender: new FormControl(''),
socialPlatforms: new FormControl([]),
addresses: new FormArray([
new FormGroup({
street: new FormControl(''),
city: new FormControl(''),
zipCode: new FormControl(''),
}),
]),
}),
});
ngOnInit() {
// Set initial data and rules
this.validator.setData(this.form.value)
.setRules(this.rules)
.setCustomMessages({
socialPlatforms: {
min: 'You must at least select :min platforms',
},
});
this.validationErrorService.setErrors(this.validator.errors());
}
onSubmit() {
// Pass the submitted form data to the validator instance and run the validation
this.validator.setData(this.form.value).validate();
}
}
<form [formGroup]="form" (ngSubmit)="onSubmit()">
<app-account></app-account>
<app-profile></app-profile>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
Account Component
- TS
- HTML
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { FormGroup, FormGroupDirective } from "@angular/forms";
import { ErrorBag } from 'simple-body-validator';
import { ValidationErrorService } from '../../services/validationError.service';
@Component({
selector: 'app-account',
templateUrl: './account.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./account.component.css']
})
export class AccountComponent implements OnInit {
form: FormGroup = new FormGroup({});
constructor(
private rootFormGroup: FormGroupDirective,
private validationErrorService: ValidationErrorService,
){}
ngOnInit(): void {
this.form = this.rootFormGroup.control;
}
get errors(): ErrorBag {
return this.validationErrorService.getErrors();
}
}
<div [formGroup]="form">
<h2>Account</h2>
<div class="mb-20">
<label class="mr-10" for="email">Email</label>
<input type="text" id="email" formControlName="email" />
<p class="cl-red" *ngIf="errors.has('email')">
{{ errors.first('email') }}
</p>
</div>
<div class="mb-20">
<label class="mr-10" for="password">Password</label>
<input type="password" id="password" formControlName="password" />
<p class="cl-red" *ngIf="errors.has('password')">
{{ errors.first('password') }}
</p>
</div>
</div>
Profile Component
- TS
- HTML
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { FormControl, FormGroup, FormGroupDirective } from "@angular/forms";
import { ErrorBag } from 'simple-body-validator';
import { ValidationErrorService } from '../../services/validationError.service';
@Component({
selector: 'app-profile',
templateUrl: './profile.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./profile.component.css']
})
export class ProfileComponent implements OnInit {
profile: FormGroup = new FormGroup({});
constructor(
private rootFormGroup: FormGroupDirective,
private validationErrorService: ValidationErrorService,
){}
ngOnInit(): void {
this.profile = this.rootFormGroup.control.get('profile') as FormGroup;
}
get errors(): ErrorBag {
return this.validationErrorService.getErrors();
}
get socialPlatforms(): FormControl {
return this.profile.get('socialPlatforms') as FormControl;
}
}
<div [formGroup]="profile">
<h2>Profile</h2>
<div class="mb-20">
<label class="mr-10" for="firstName">First Name</label>
<input type="text" id="firstName" formControlName="firstName" />
<p class="cl-red" *ngIf="errors.has('profile.firstName')">
{{ errors.first('profile.firstName') }}
</p>
</div>
<div class="mb-20">
<label class="mr-10" for="lastName">Last Name</label>
<input type="text" id="lastName" formControlName="lastName" />
<p class="cl-red" *ngIf="errors.has('profile.lastName')">
{{ errors.first('profile.lastName') }}
</p>
</div>
<app-gender ></app-gender>
<app-social-platform
[selectedPlatforms]="socialPlatforms.value"
(onChangeEvent)="socialPlatforms.setValue($event)"
>
</app-social-platform>
<app-addresses-list> </app-addresses-list>
</div>
warning
The Profile component will not work directly since we didn't create the Gender, SocialPlatform, and AddressesList components yet.
If you take a look at the HTML part of the Profile component, you will notice that when we checked if the error exist
we followed the same path specified in the rules object.
<p *ngIf="errors.has('profile.firstName')">{{ errors.first('profile.firstName') }}</p>
Gender Component
- TS
- HTML
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { FormGroup, FormGroupDirective } from "@angular/forms";
import { ErrorBag } from 'simple-body-validator';
import { ValidationErrorService } from '../../services/validationError.service';
@Component({
selector: 'app-gender',
templateUrl: './gender.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./gender.component.css']
})
export class GenderComponent implements OnInit {
profile: FormGroup = new FormGroup({});
genderList: string[] = [
'Female', 'Male', 'Other'
];
constructor(
private rootFormGroup: FormGroupDirective,
private validationErrorService: ValidationErrorService,
){}
ngOnInit(): void {
this.profile = this.rootFormGroup.control;
}
get errors(): ErrorBag {
return this.validationErrorService.getErrors();
}
}
<div [formGroup]="profile" class="mb-20">
<label for="gender" class="mr-10">Gender</label>
<ng-container *ngFor="let gender of genderList">
<input
type="radio"
[id]="gender"
[value]="gender"
formControlName="gender"
/>
<label [for]="gender" class="mr-10">{{ gender }}</label>
</ng-container>
<p class="cl-red" *ngIf="errors.has('profile.gender')">
{{ errors.first('profile.gender') }}
</p>
</div>
SocialPlatform Component
- TS
- HTML
import { Component, Input, Output, EventEmitter } from '@angular/core';
import { ErrorBag } from 'simple-body-validator';
import { ValidationErrorService } from '../../services/validationError.service';
@Component({
selector: 'app-social-platform',
templateUrl: './socialPlatform.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./socialPlatform.component.css']
})
export class SocialPLatformComponent {
@Input() selectedPlatforms: string[] = [];
@Output() onChangeEvent = new EventEmitter<string[]>();
platforms: string[] = [
'Facebook', 'Instagram', 'Twitter', 'Linkedin'
];
constructor(
private validationErrorService: ValidationErrorService
) {}
get errors(): ErrorBag {
return this.validationErrorService.getErrors();
}
handleChange(event: Event): void {
const target = event.target as HTMLInputElement;
const { checked, value} = target;
if (checked) {
// Add the new value to selected platforms list
this.onChangeEvent.emit([ ...this.selectedPlatforms, value]);
} else {
// Remove the value from the selected platform list
this.onChangeEvent.emit(
[
...this.selectedPlatforms.splice(this.selectedPlatforms.indexOf(value))
]
);
}
}
}
<div class="mb-20">
<h5>Social PLatforms</h5>
<div>
<ng-container *ngFor="let platform of platforms">
<input
type="checkbox"
[id]="platform"
[value]="platform"
class="mr-10"
[checked]="selectedPlatforms.indexOf(platform) !== -1"
(change)="handleChange($event)"
/>
<label class="mr-10" [for]="platform">{{ platform }}</label>
</ng-container>
<p class="cl-red" *ngIf="errors.has('profile.socialPlatforms')">
{{ errors.first('profile.socialPlatforms') }}
</p>
</div>
</div>
AddressesList Component
- TS
- HTML
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { FormGroup, FormGroupDirective, FormArray, FormControl } from "@angular/forms";
import { ErrorBag } from 'simple-body-validator';
import { ValidationErrorService } from '../../services/validationError.service';
@Component({
selector: 'app-addresses-list',
templateUrl: './addressesList.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./addressesList.component.css']
})
export class AddressesList implements OnInit {
addresses: FormArray = new FormArray([]);
constructor(
private rootFormGroup: FormGroupDirective,
private validationErrorService: ValidationErrorService,
) {}
ngOnInit(): void {
this.addresses = this.rootFormGroup.control.get('addresses') as FormArray;
}
get errors(): ErrorBag {
return this.validationErrorService.getErrors();
}
addAddress() {
this.addresses.push(new FormGroup({
street: new FormControl(''),
city: new FormControl(''),
zipCode: new FormControl(''),
}));
}
removeAddress() {
const index = this.addresses.length - 1;
// Remove the errors related to the address fields
this.errors.clear([
`profile.addresses.${index}.city`,
`profile.addresses.${index}.street`,
`profile.addresses.${index}.zipCode`
]);
this.addresses.removeAt(index);
}
}
<div class="mb-20" >
<h2>Address</h2>
<div *ngFor="let address of addresses.controls; let i = index">
<app-address [index]="i"></app-address>
</div>
<button
*ngIf="addresses.controls.length < 3"
class="mr-20"
type="button"
(click)="addAddress()"
>
Add Address
</button>
<button
*ngIf="addresses.length > 1"
type="button"
(click)="removeAddress()"
>
Remove Address
</button>
</div>
In the example above, the index value was passed from the AddressesList component into the Address component.
The index will be used to identify the appropriate input values and error messages associated with each address.
Address Component
- TS
- HTML
import { Component, OnInit, Input } from '@angular/core';
import { FormGroup, FormGroupDirective } from "@angular/forms";
import { ErrorBag } from 'simple-body-validator';
import { ValidationErrorService } from '../../services/validationError.service';
@Component({
selector: 'app-address',
templateUrl: './address.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./address.component.css']
})
export class Address implements OnInit {
@Input() index;
address: FormGroup = new FormGroup({});
constructor(
private rootFormGroup: FormGroupDirective,
private validationErrorService: ValidationErrorService,
) {}
ngOnInit(): void {
this.address = this.rootFormGroup.control.get(`addresses.${this.index}`) as FormGroup;
}
get errors(): ErrorBag {
return this.validationErrorService.getErrors();
}
}
<div [formGroup]="address">
<h5>Address {{ index + 1 }}</h5>
<div class="mb-20">
<label class="mr-10" [for]="'street' + index">Street</label>
<input
[id]="'street' + index"
formControlName="street"
type="text"
/>
<p class="cl-red" *ngIf="errors.has('profile.addresses.' + index + '.street')">
{{ errors.first('profile.addresses.' + index + '.street') }}
</p>
</div>
<div class="mb-20">
<label class="mr-10" [for]="'city' + index">City</label>
<input
[id]="'city' + index"
formControlName="city"
type="text"
/>
<p class="cl-red" *ngIf="errors.has('profile.addresses.' + index + '.city')">
{{ errors.first('profile.addresses.' + index + '.city') }}
</p>
</div>
<div class="mb-20">
<label class="mr-10" [for]="'zipCode' + index">Zip Code</label>
<input
[id]="'zipCode' + index"
formControlName="zipCode"
type="text"
/>
<p class="cl-red" *ngIf="errors.has('profile.addresses.' + index + '.zipCode')">
{{ errors.first('profile.addresses.' + index + '.zipCode') }}
</p>
</div>
</div>
To be able to get the correct error message for the fields in the address component, we followed the same path
of the rules object, and we replaced * with the index of the array.
profile: {
'addresses.*.street': 'required|string|min:5|max:255',
}
errors.first(`profile.addresses.${index}.street`);